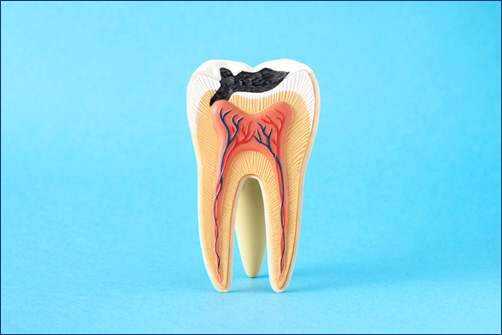
Tooth decay is a common dental issue that affects people of all ages. It occurs when the hard outer layer of the teeth, known as enamel, is damaged by acids produced by bacteria in the mouth. If left untreated, tooth decay can lead to cavities, pain, and even tooth loss. Understanding the causes, prevention strategies, and treatment options for cavities can help you maintain optimal oral health and prevent future dental problems.
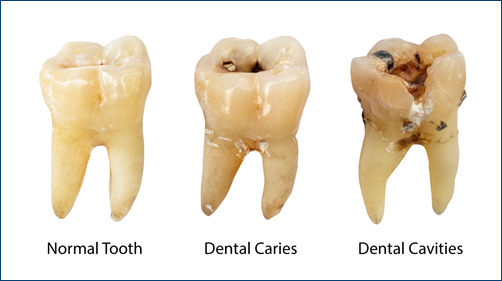 Causes of Tooth Decay
Causes of Tooth Decay
- Bacterial Plaque: The primary cause of tooth decay is the accumulation of plaque. Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth. When you consume sugary or starchy foods, the bacteria in plaque produce acids that attack the enamel. This leads to demineralization and the formation of cavities over time.
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing allow plaque to build up on the teeth, increasing the risk of decay. Without proper oral hygiene, plaque hardens into tartar, which can only be removed by a dental professional and can further contribute to tooth decay and gum disease.
- Dietary Habits: Frequent consumption of sugary and acidic foods and beverages can accelerate the decay process. Sweets, sodas, and fruit juices create an environment in which bacteria thrive, producing acids that erode the enamel.
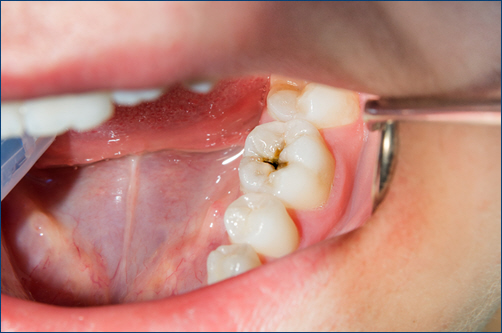 Prevention of Tooth Decay
Prevention of Tooth Decay
- Good Oral Hygiene Practices: Brushing your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and flossing daily are essential for removing plaque and preventing cavities. Using an antimicrobial mouthwash can also help reduce the bacterial load in the mouth.
- Regular Dental Check-Ups: Visiting your dentist regularly for cleanings and check-ups is crucial for early detection and prevention of tooth decay. Professional cleanings remove tartar and plaque that are difficult to eliminate with regular brushing and flossing.
- Healthy Diet Choices: Limiting sugary and acidic foods and drinks can significantly reduce the risk of tooth decay. Instead, opt for a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and dairy products that provide essential nutrients for strong teeth.
Treatment for Cavities
- Dental Fillings: When a cavity forms, the most common treatment is a dental filling. The dentist removes the decayed portion of the tooth and fills the space with a material such as composite resin, amalgam, or porcelain to restore its shape and function.
- Crowns: For larger cavities or extensive decay, a crown may be necessary to protect and strengthen the damaged tooth. A crown is a custom-made cap that covers the entire tooth, providing durability and stability.
- Root Canal Therapy: If decay reaches the pulp of the tooth, causing infection, a root canal may be needed. This procedure involves removing the infected tissue, cleaning the root canals, and sealing them to prevent further infection, ultimately saving the tooth from extraction.
Tooth decay is a preventable dental issue that, if left untreated, can lead to significant oral health problems. By practicing good oral hygiene, making healthy dietary choices, and visiting your dentist regularly, you can reduce your risk of cavities and maintain a healthy smile. If you suspect you have a cavity, seeking prompt treatment can prevent further complications and preserve your dental health for years to come.