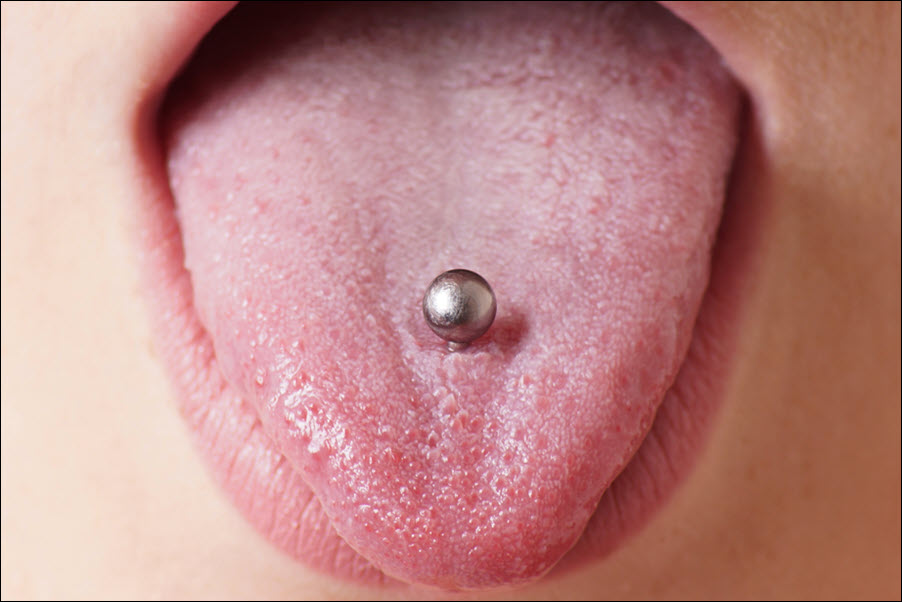
Oral piercings create unique dental health risks. Piercings in the tongue, lips, or cheeks increase the risk of infection and damage. Metal jewelry can chip teeth, irritate gums, and cause nerve damage. Oral piercings also increase the risk of gum recession and tooth sensitivity. Poor healing and infection cause swelling and difficulty speaking or eating. Long-term complications include tooth misalignment and increased plaque buildup. Proper care and professional monitoring reduce these risks and improve healing. Understanding the dangers of oral piercings protects your dental health and smile strength. Let’s explore the dental risks of oral piercings and how to prevent damage.
Increased Risk of Infection
Oral piercings increase the risk of bacterial infections. The mouth contains thousands of bacteria, which enter the piercing site during healing. Poor cleaning habits increase the risk of swelling and inflammation. An infected piercing causes redness, pain, and pus discharge. Severe infections spread to the jaw and bloodstream, increasing health complications. Biting or playing with the piercing increases bacterial exposure. Infection increases gum sensitivity and weakens tooth support. Cleaning the piercing with saltwater and antibacterial mouthwash reduces infection risk. Professional monitoring ensures proper healing and reduces inflammation. Reducing infection risk strengthens gum health and improves oral comfort. Proper care protects against bacterial infections and tooth damage.
Tooth Chipping and Enamel Damage
 Metal jewelry increases the risk of tooth chipping and enamel fractures. Biting down on a tongue or lip ring damages enamel and increases sensitivity. Fractured enamel exposes dentin, increasing cavity risk and nerve sensitivity. Repeated contact with metal piercings weakens tooth structure and increases cracks. Chipped teeth require dental bonding, crowns, or veneers to restore strength. Hard piercings also damage fillings, causing them to loosen or break. Avoiding biting or playing with the piercing reduces the risk of enamel damage. Wearing soft, non-metallic jewelry reduces chipping risk. Professional dental care restores chipped enamel and improves tooth strength. Protecting enamel increases tooth durability and reduces sensitivity.
Metal jewelry increases the risk of tooth chipping and enamel fractures. Biting down on a tongue or lip ring damages enamel and increases sensitivity. Fractured enamel exposes dentin, increasing cavity risk and nerve sensitivity. Repeated contact with metal piercings weakens tooth structure and increases cracks. Chipped teeth require dental bonding, crowns, or veneers to restore strength. Hard piercings also damage fillings, causing them to loosen or break. Avoiding biting or playing with the piercing reduces the risk of enamel damage. Wearing soft, non-metallic jewelry reduces chipping risk. Professional dental care restores chipped enamel and improves tooth strength. Protecting enamel increases tooth durability and reduces sensitivity.
Gum Recession and Gum Damage
Lip and tongue piercings rub against gum tissue, causing irritation and recession. Constant friction weakens gum attachment and increases sensitivity. Receding gums expose tooth roots, increasing plaque buildup and cavity risk. Metal jewelry creates pressure on gum tissue, causing inflammation and soreness. Severe gum recession leads to tooth misalignment and tooth loss. Proper jewelry positioning reduces gum irritation and recession risk. Regular dental checkups monitor gum health and detect early signs of damage. Avoiding large or heavy jewelry reduces gum strain and inflammation. Stronger gums improve tooth stability and bite strength. Protecting gum health increases overall dental comfort and strength.
Nerve Damage and Loss of Sensation
Oral piercings increase the risk of nerve damage. Improper piercing placement affects nerves, reducing sensation in the tongue or lips. Nerve damage causes numbness, tingling, or loss of taste. Severe nerve damage affects speech clarity and chewing comfort. Damaged nerves increase difficulty in detecting hot, cold, and sweet foods. Professional piercing placement reduces the risk of nerve injury. Dentists monitor nerve health and provide treatments for sensitivity issues. Damaged nerves take months to heal or may remain permanently affected. Avoiding repeated pressure on the piercing reduces nerve strain. Protecting nerve health increases mouth comfort and sensory strength. Stronger nerves improve overall mouth function and comfort.
Excessive Saliva Production and Speech Issues
Tongue and lip piercings increase saliva production. Increased saliva flow creates difficulty with speech and swallowing. Excess saliva increases plaque formation and bacterial growth. Metal jewelry interferes with tongue movement, reducing speech clarity. Improper piercing size affects tongue positioning and muscle strength. Professional monitoring ensures proper jewelry fit and mouth function. Consistent practice improves speech clarity and muscle strength. Rinsing with mouthwash reduces plaque buildup and improves breath freshness. Better saliva control reduces speech problems and improves chewing comfort. Managing saliva production increases overall mouth function and comfort. Stronger oral muscles improve speech and bite strength.
Long-Term Risks of Oral Piercings
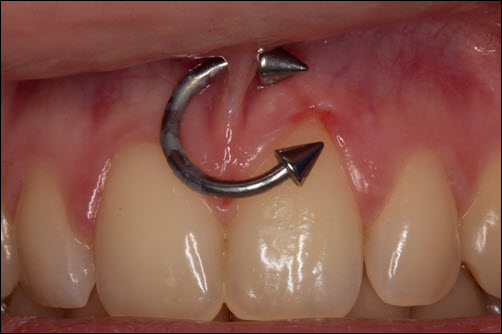 Oral piercings create long-term dental complications. Gum recession increases the risk of tooth sensitivity and misalignment. Enamel erosion increases cavity formation and weakens tooth structure. Nerve damage reduces tongue strength and muscle coordination. Misaligned teeth create bite imbalance and increased grinding pressure. Poorly healed piercings increase the risk of chronic infections and inflammation. Regular dental monitoring detects early signs of damage and sensitivity. Removing problematic piercings improves gum health and tooth stability. Proper care and professional cleanings reduce long-term damage and improve recovery. Protecting enamel and gums increases long-term dental strength and comfort. Early detection reduces long-term complications and improves dental health.
Oral piercings create long-term dental complications. Gum recession increases the risk of tooth sensitivity and misalignment. Enamel erosion increases cavity formation and weakens tooth structure. Nerve damage reduces tongue strength and muscle coordination. Misaligned teeth create bite imbalance and increased grinding pressure. Poorly healed piercings increase the risk of chronic infections and inflammation. Regular dental monitoring detects early signs of damage and sensitivity. Removing problematic piercings improves gum health and tooth stability. Proper care and professional cleanings reduce long-term damage and improve recovery. Protecting enamel and gums increases long-term dental strength and comfort. Early detection reduces long-term complications and improves dental health.
Preventing Dental Damage from Oral Piercings
Proper care reduces dental damage from oral piercings. Clean the piercing site with saltwater or antibacterial mouthwash daily. Avoid biting or playing with the piercing to prevent chipping and enamel damage. Use soft, non-metallic jewelry to reduce gum irritation and tooth wear. Visit your dentist regularly to monitor gum health and enamel strength. Professional cleanings remove plaque buildup and improve tooth surface strength. Avoiding hard or sticky foods reduces chipping and gum strain. Wearing a mouthguard during sports protects piercings and teeth from impact damage. Proper care increases healing speed and reduces dental complications. Protecting enamel and gums improves long-term oral health.
Boosting Confidence with a Healthy Smile
Protecting dental health increases smile strength and confidence. Stronger teeth improve chewing comfort and speech clarity. Reduced plaque buildup increases breath freshness and mouth comfort. Balanced gumlines improve smile symmetry and facial balance. Reduced tooth sensitivity increases comfort while eating and speaking. Stronger enamel resists cracking and chipping from piercing pressure. Reduced inflammation increases gum strength and bite stability. Healthier gums and teeth improve social and professional confidence. Better dental health increases long-term comfort and smile strength. A confident smile improves personal and social interactions. Protecting teeth and gums increases comfort and overall dental strength.
Oral piercings create unique dental health risks, including enamel damage, gum recession, and infection. Proper care and regular dental monitoring reduce these risks. Brushing and flossing daily protect gums and teeth from plaque buildup. Professional cleanings improve tooth strength and reduce gum inflammation. Removing problematic piercings reduces long-term dental complications. Choosing soft, non-metallic jewelry reduces the risk of chipping and sensitivity. Protecting nerves and gum tissue improves mouth function and comfort. Investing in better oral care increases dental strength and smile confidence. A balanced, healthy smile improves both comfort and appearance. Proper dental care reduces risks and strengthens overall oral health.